Quantitative Targeted Proteomic Analysis Technology
Fumio MATSUDA
Graduate School of Information Science and Technology, Osaka University


Fumio MATSUDA
Graduate School of Information Science and Technology, Osaka University


We developed a method of highly sensitive simultaneous quantitation of the expression levels of dozens of proteins in smart cells. We have completed the construction of multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) assay methods for main metabolic enzyme proteins, such as E. coli, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Corynebacterium glutamicum and oleaginous yeasts. We have built a database of MRM assay methods constructed in the Smartcell Project.
The Smartcell Project requires rational modifications of metabolic pathways in order to maximize the material production capability of cells. To modify metabolic pathways, the expression levels of enzyme proteins are increased or decreased by artificially modifying the genome of the host microorganism. Since the protein amount in cells involves various factors associated with transcription, translation and proteolysis, it is necessary to have a measurement method for rapidly evaluating whether the amount of enzyme protein has been adjusted as designed. Under these circumstances, we focused on the high-accuracy quantitative targeted proteomic analysis as an optimal method for the evaluation of smart cells. In this method, a trypsin-digested peptide mixture is separated by liquid chromatography and analyzed in the multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode of a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer. We are developing a targeted proteomic analysis system authentically made in Japan, in collaboration with Shimadzu Corporation (Fig. 1).
The sample pretreatment was started with a crude protein extract of about 100 μL containing 50 μg of total proteins. After a reductive alkylation of this extract, trypsin digestion is performed overnight, and the resulting trypsin-digested peptides are desalted by solid phase extraction. We have confirmed that the pretreatment method for Saccharomyces cerevisiae is effective against various useful microorganisms, such as oleaginous yeasts, E. coli and Corynebacterium glutamicum. Data were obtained by nano-LC-MS/MS (LCMS-8060, Shimadzu Corporation). This system achieved a throughput of a sample size of 20 to 30, which is the size of a general analysis project, in about 2 days.
We have completed the construction of MRM assay methods for main metabolic enzyme proteins, such as E. coli, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Corynebacterium glutamicum and oleaginous yeasts. In addition, we are building a database of the MRM assay methods constructed, so as to establish a platform that can be customized as required.
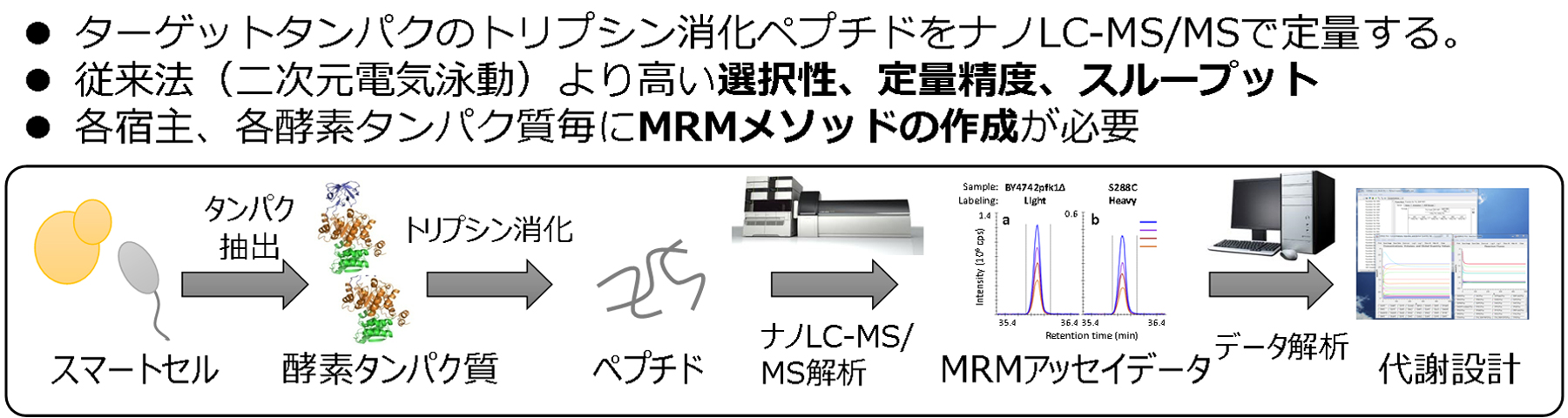
This technology allows highly sensitive simultaneous quantitation of the expression levels of dozens of proteins.
Antibody preparation is not required.
1) F. Matsuda et al. : Mass Spectrometry, 6(1), A0056 (2017)
Last updated:December 25, 2023